|
对于最新稳定版本,请使用Spring Batch Documentation 6.0.0! |
子元素
当这时网关正在接收来自Pollable频道你必须提供
全球违约轮询器或提供轮询器子元素到职位启动网关.
-
Java
-
XML
以下示例展示了如何在 Java 中提供轮询器:
@Bean
@ServiceActivator(inputChannel = "queueChannel", poller = @Poller(fixedRate="1000"))
public JobLaunchingGateway sampleJobLaunchingGateway() {
JobLaunchingGateway jobLaunchingGateway = new JobLaunchingGateway(jobLauncher());
jobLaunchingGateway.setOutputChannel(replyChannel());
return jobLaunchingGateway;
}以下示例展示了如何用XML提供轮询器:
<batch-int:job-launching-gateway request-channel="queueChannel"
reply-channel="replyChannel" job-launcher="jobLauncher">
<int:poller fixed-rate="1000">
</batch-int:job-launching-gateway>提供信息信息反馈
因为春批作业可以运行较长时间,从而提供进展 信息往往至关重要。例如,利益相关者可能希望 如果批处理作业的部分或全部部分失败,将收到通知。 Spring Batch 为收集这些信息提供了支持 通过:
-
主动投票
-
事件驱动听众
在异步启动春批作业时(例如,使用作业启动)
门户),a作业执行实例被返回。因此,你可以使用JobExecution.getJobId()通过检索更新的实例,持续轮询状态更新作业执行来自JobRepository通过使用JobExplorer.然而,这个
被认为是次优方法,更倾向于事件驱动的方法。
因此,春批为听众提供了包括最常用的三种听众 听众:
-
StepListener(听音器) -
ChunkListener(分块听众) -
JobExecutionListener
在下图示例中,一个 Spring Batch 作业被配置为StepExecutionListener.因此,Spring Integration 会接收并处理之前的任何步骤
或者事后。例如,你可以检查收到的步执行通过使用路由器.根据检查结果,可能会发生各种情况(例如:
将消息路由到邮件外发通道适配器),以便电子邮件通知能够
根据某种条件被派遣。
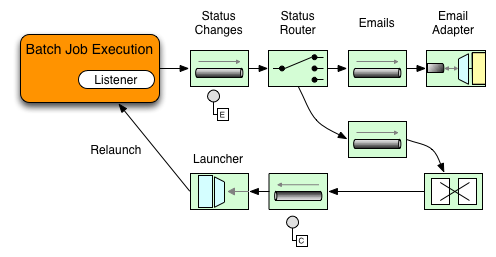
以下两部分示例展示了监听者如何配置发送
致网关对于步执行事件并记录其输出为日志通道适配器.
首先,创建通知集成豆。
-
Java
-
XML
以下示例展示了如何在 Java 中创建通知集成 Beans:
@Bean
@ServiceActivator(inputChannel = "stepExecutionsChannel")
public LoggingHandler loggingHandler() {
LoggingHandler adapter = new LoggingHandler(LoggingHandler.Level.WARN);
adapter.setLoggerName("TEST_LOGGER");
adapter.setLogExpressionString("headers.id + ': ' + payload");
return adapter;
}
@MessagingGateway(name = "notificationExecutionsListener", defaultRequestChannel = "stepExecutionsChannel")
public interface NotificationExecutionListener extends StepExecutionListener {}你需要添加@IntegrationComponentScan对你的配置进行注释。 |
以下示例展示了如何用XML创建通知集成豆子:
<int:channel id="stepExecutionsChannel"/>
<int:gateway id="notificationExecutionsListener"
service-interface="org.springframework.batch.core.StepExecutionListener"
default-request-channel="stepExecutionsChannel"/>
<int:logging-channel-adapter channel="stepExecutionsChannel"/>其次,修改你的工作,增加一个步级监听器。
-
Java
-
XML
以下示例展示了如何在 Java 中添加步级监听器:
public Job importPaymentsJob(JobRepository jobRepository, PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager) {
return new JobBuilder("importPayments", jobRepository)
.start(new StepBuilder("step1", jobRepository)
.chunk(200, transactionManager)
.listener(notificationExecutionsListener())
// ...
.build();
)
.build();
}以下示例展示了如何在 XML 中添加步级监听器:
<job id="importPayments">
<step id="step1">
<tasklet ../>
<chunk ../>
<listeners>
<listener ref="notificationExecutionsListener"/>
</listeners>
</tasklet>
...
</step>
</job>异步处理器
异步处理器帮助你扩展项目处理。在异步中
处理器使用场景,一种异步项目处理器作为调度器,执行 的逻辑
这ItemProcessor针对新帖子中的某个项目。一旦物品完成,前途是
传给异步项目写手待书写。
因此,你可以通过使用异步项目处理来提升性能,基本上
允许你实现分叉-连接场景。这异步项目写手收集结果,
一旦所有结果可用,就会写回该区块。
-
Java
-
XML
以下示例展示了如何配置异步项目处理器在爪哇语中:
@Bean
public AsyncItemProcessor processor(ItemProcessor itemProcessor, TaskExecutor taskExecutor) {
AsyncItemProcessor asyncItemProcessor = new AsyncItemProcessor();
asyncItemProcessor.setTaskExecutor(taskExecutor);
asyncItemProcessor.setDelegate(itemProcessor);
return asyncItemProcessor;
}以下示例展示了如何配置异步项目处理器以XML形式表示:
<bean id="processor"
class="org.springframework.batch.integration.async.AsyncItemProcessor">
<property name="delegate">
<bean class="your.ItemProcessor"/>
</property>
<property name="taskExecutor">
<bean class="org.springframework.core.task.SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor"/>
</property>
</bean>这委托财产指的是你的ItemProcessor豆子,以及任务执行者属性指的是任务执行者由你选择。
-
Java
-
XML
以下示例展示了如何配置异步项目写手在爪哇语中:
@Bean
public AsyncItemWriter writer(ItemWriter itemWriter) {
AsyncItemWriter asyncItemWriter = new AsyncItemWriter();
asyncItemWriter.setDelegate(itemWriter);
return asyncItemWriter;
}以下示例展示了如何配置异步项目写手以XML形式表示:
<bean id="itemWriter"
class="org.springframework.batch.integration.async.AsyncItemWriter">
<property name="delegate">
<bean id="itemWriter" class="your.ItemWriter"/>
</property>
</bean>再说一次,委托财产是
实际上是对你ItemWriter豆。
外部化批处理过程执行
迄今讨论的集成方法提出了应用场景 其中 Spring Integration 将 Spring Batch 包裹为外壳。 不过,Spring Batch 也可以在内部使用 Spring Integration。 通过这种方法,Spring Batch用户可以委派 将物品甚至块处理给外部进程。这 让你分担复杂的处理。Spring Batch集成 为以下项目提供专门支持:
-
远程分块
-
远程分区
远程分块
下图展示了使用 Spring Batch 时远程分块的一种工作方式 结合春季集成:
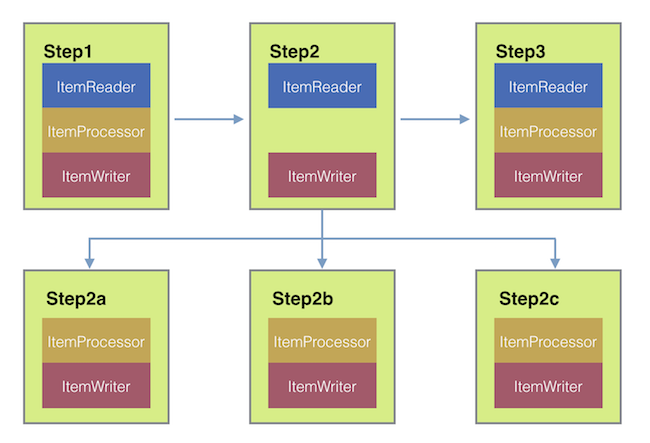
更进一步,你还可以将
通过使用区块消息频道项目写作(由 Spring Batch Integration 提供),发送项目
并收集结果。发送后,Spring Batch继续
阅读和分组项目的过程,无需等待结果。
相反,这是区块消息频道项目写作收集结果并重新整合进Spring Batch流程。
有了Spring Integration,你拥有完整的
对进程并发的控制(例如,由
使用队列通道而不是直达频道).此外,通过依赖
Spring Integration 丰富的通道适配器集合(例如
JMS 和 AMQP),你可以将批处理作业的块分发到
外部处理系统。
-
Java
-
XML
一个需要远程分块的步骤作业可能配置类似于 以下是爪哇语:
public Job chunkJob(JobRepository jobRepository, PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager) {
return new JobBuilder("personJob", jobRepository)
.start(new StepBuilder("step1", jobRepository)
.<Person, Person>chunk(200, transactionManager)
.reader(itemReader())
.writer(itemWriter())
.build())
.build();
}一个需要远程分块的步骤作业可能配置类似于 以下以XML形式:
<job id="personJob">
<step id="step1">
<tasklet>
<chunk reader="itemReader" writer="itemWriter" commit-interval="200"/>
</tasklet>
...
</step>
</job>这ItemReader你想用来读取数据的豆子的参考点
经理。这ItemWriter参考指向特殊ItemWriter(称为区块消息频道项目写作),如前所述。处理器(如果有的话)则被遗漏
管理器配置,就像在工作者上配置的那样。你应该检查任何
实现时还要添加额外的组件属性,如节气门限制等
你的使用场景。
-
Java
-
XML
以下 Java 配置提供了基本的管理器设置:
@Bean
public org.apache.activemq.ActiveMQConnectionFactory connectionFactory() {
ActiveMQConnectionFactory factory = new ActiveMQConnectionFactory();
factory.setBrokerURL("tcp://localhost:61616");
return factory;
}
/*
* Configure outbound flow (requests going to workers)
*/
@Bean
public DirectChannel requests() {
return new DirectChannel();
}
@Bean
public IntegrationFlow outboundFlow(ActiveMQConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {
return IntegrationFlow
.from(requests())
.handle(Jms.outboundAdapter(connectionFactory).destination("requests"))
.get();
}
/*
* Configure inbound flow (replies coming from workers)
*/
@Bean
public QueueChannel replies() {
return new QueueChannel();
}
@Bean
public IntegrationFlow inboundFlow(ActiveMQConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {
return IntegrationFlow
.from(Jms.messageDrivenChannelAdapter(connectionFactory).destination("replies"))
.channel(replies())
.get();
}
/*
* Configure the ChunkMessageChannelItemWriter
*/
@Bean
public ItemWriter<Integer> itemWriter() {
MessagingTemplate messagingTemplate = new MessagingTemplate();
messagingTemplate.setDefaultChannel(requests());
messagingTemplate.setReceiveTimeout(2000);
ChunkMessageChannelItemWriter<Integer> chunkMessageChannelItemWriter
= new ChunkMessageChannelItemWriter<>();
chunkMessageChannelItemWriter.setMessagingOperations(messagingTemplate);
chunkMessageChannelItemWriter.setReplyChannel(replies());
return chunkMessageChannelItemWriter;
}以下 XML 配置提供了基本的管理器设置:
<bean id="connectionFactory" class="org.apache.activemq.ActiveMQConnectionFactory">
<property name="brokerURL" value="tcp://localhost:61616"/>
</bean>
<int-jms:outbound-channel-adapter id="jmsRequests" destination-name="requests"/>
<bean id="messagingTemplate"
class="org.springframework.integration.core.MessagingTemplate">
<property name="defaultChannel" ref="requests"/>
<property name="receiveTimeout" value="2000"/>
</bean>
<bean id="itemWriter"
class="org.springframework.batch.integration.chunk.ChunkMessageChannelItemWriter"
scope="step">
<property name="messagingOperations" ref="messagingTemplate"/>
<property name="replyChannel" ref="replies"/>
</bean>
<int:channel id="replies">
<int:queue/>
</int:channel>
<int-jms:message-driven-channel-adapter id="jmsReplies"
destination-name="replies"
channel="replies"/>上述配置提供了若干豆子。我们
通过使用 ActiveMQ 配置我们的消息中间件和
由Spring Integration提供的进站和出站JMS适配器。如
显示,我们的itemWriter豆子,也就是
由我们的工作步骤引用,使用以下区块消息频道项目写作在
配置好的中间件。
现在我们可以进入工人配置,如下示例所示:
-
Java
-
XML
以下示例展示了Java中的工作者配置:
@Bean
public org.apache.activemq.ActiveMQConnectionFactory connectionFactory() {
ActiveMQConnectionFactory factory = new ActiveMQConnectionFactory();
factory.setBrokerURL("tcp://localhost:61616");
return factory;
}
/*
* Configure inbound flow (requests coming from the manager)
*/
@Bean
public DirectChannel requests() {
return new DirectChannel();
}
@Bean
public IntegrationFlow inboundFlow(ActiveMQConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {
return IntegrationFlow
.from(Jms.messageDrivenChannelAdapter(connectionFactory).destination("requests"))
.channel(requests())
.get();
}
/*
* Configure outbound flow (replies going to the manager)
*/
@Bean
public DirectChannel replies() {
return new DirectChannel();
}
@Bean
public IntegrationFlow outboundFlow(ActiveMQConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {
return IntegrationFlow
.from(replies())
.handle(Jms.outboundAdapter(connectionFactory).destination("replies"))
.get();
}
/*
* Configure the ChunkProcessorChunkHandler
*/
@Bean
@ServiceActivator(inputChannel = "requests", outputChannel = "replies")
public ChunkProcessorChunkHandler<Integer> chunkProcessorChunkHandler() {
ChunkProcessor<Integer> chunkProcessor
= new SimpleChunkProcessor<>(itemProcessor(), itemWriter());
ChunkProcessorChunkHandler<Integer> chunkProcessorChunkHandler
= new ChunkProcessorChunkHandler<>();
chunkProcessorChunkHandler.setChunkProcessor(chunkProcessor);
return chunkProcessorChunkHandler;
}以下示例展示了 XML 中的工作配置:
<bean id="connectionFactory" class="org.apache.activemq.ActiveMQConnectionFactory">
<property name="brokerURL" value="tcp://localhost:61616"/>
</bean>
<int:channel id="requests"/>
<int:channel id="replies"/>
<int-jms:message-driven-channel-adapter id="incomingRequests"
destination-name="requests"
channel="requests"/>
<int-jms:outbound-channel-adapter id="outgoingReplies"
destination-name="replies"
channel="replies">
</int-jms:outbound-channel-adapter>
<int:service-activator id="serviceActivator"
input-channel="requests"
output-channel="replies"
ref="chunkProcessorChunkHandler"
method="handleChunk"/>
<bean id="chunkProcessorChunkHandler"
class="org.springframework.batch.integration.chunk.ChunkProcessorChunkHandler">
<property name="chunkProcessor">
<bean class="org.springframework.batch.core.step.item.SimpleChunkProcessor">
<property name="itemWriter">
<bean class="io.spring.sbi.PersonItemWriter"/>
</property>
<property name="itemProcessor">
<bean class="io.spring.sbi.PersonItemProcessor"/>
</property>
</bean>
</property>
</bean>这些配置项目大多应该看起来很熟悉
管理器配置。工人不需要访问
Spring BatchJobRepository也不
到实际的作业配置文件。主要关注的Beans
是chunkProcessorChunkHandler.这块处理器的属性块处理器块处理器需要一个
配置SimpleChunk处理器,这就是你会给你引用的地方ItemWriter(还有,可选的,你的ItemProcessor)该程序将运行在工人身上
当它从管理器那里收到块时。
更多信息请参见“可扩展性”章节中关于远程分块的部分。
从4.1版本开始,春季批分集成引入了@EnableBatchIntegration注释可以用来简化远程分块设置。该注释提供
有两个豆子可以在你的应用环境中自动接线:
-
RemoteChunkingManagerStepBuilderFactory: 配置管理器步骤 -
远程分块工人构建器: 配置远程工作者整合流程
这些API负责配置多个组件,如下图所示:
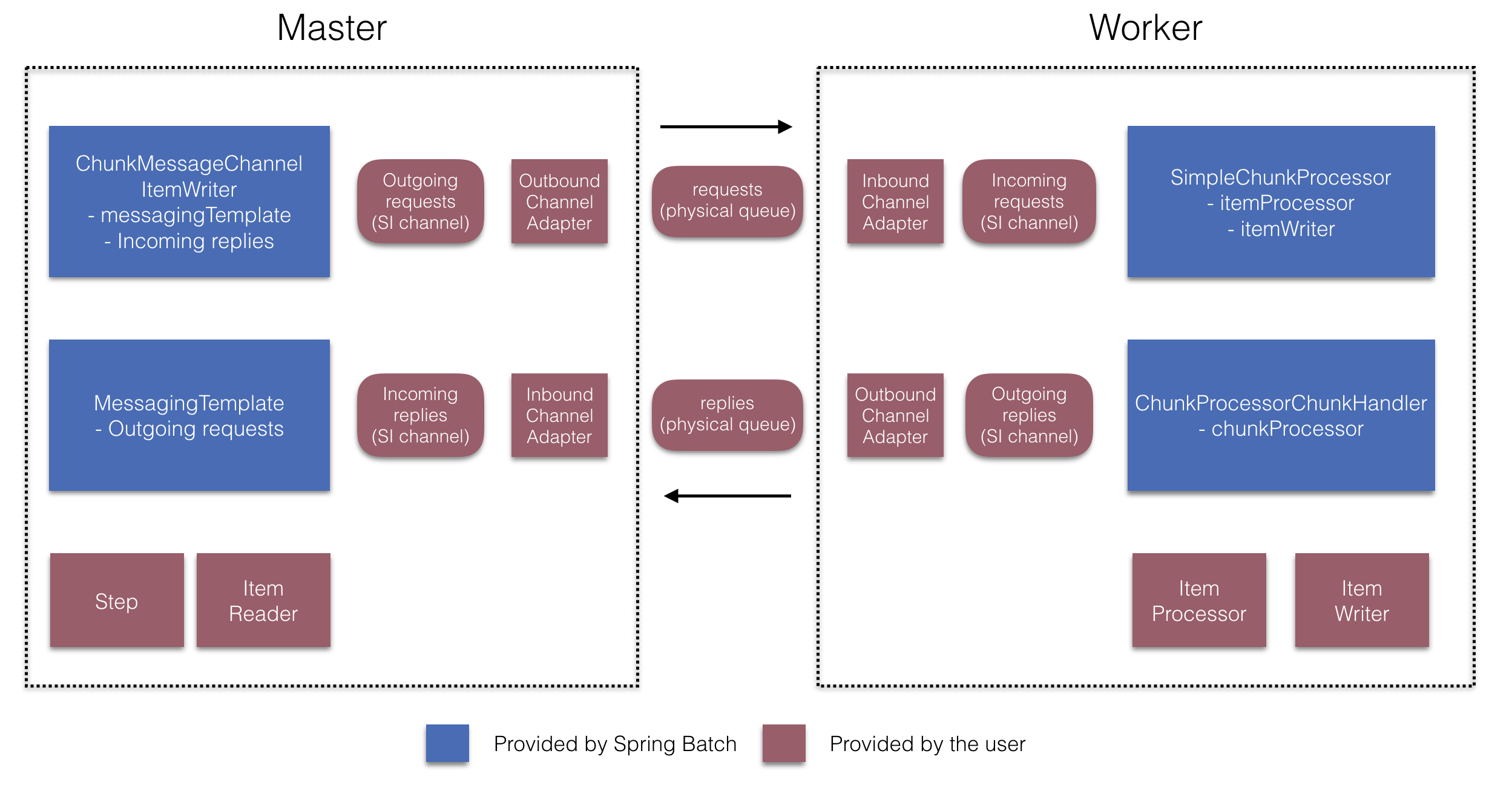
在经理方面,RemoteChunkingManagerStepBuilderFactory让你
通过声明配置管理器步骤:
-
物品读取器用于读取物品并发送给工人
-
输出通道(“外发请求”)用于向工作者发送请求
-
输入信道(“收到回复”)用于接收来自工人的回复
你不需要明确配置区块消息频道项目写作以及消息模板.
(如果有理由,你仍然可以显式配置它们。)
在工人方面,远程分块工人构建器允许你配置工人:
-
监听管理器在输入通道发送的请求(“入站请求”)
-
呼叫
手柄块方法块处理器块处理器针对每个请求 配置后ItemProcessor和ItemWriter -
在输出通道上向管理器发送回复(“发出回复”)
你不必显式配置SimpleChunk处理器以及块处理器块处理器.(如果你发现,仍然可以显式配置它们
有理由这么做)。
以下示例展示了如何使用这些 API:
@EnableBatchIntegration
@EnableBatchProcessing
public class RemoteChunkingJobConfiguration {
@Configuration
public static class ManagerConfiguration {
@Autowired
private RemoteChunkingManagerStepBuilderFactory managerStepBuilderFactory;
@Bean
public TaskletStep managerStep() {
return this.managerStepBuilderFactory.get("managerStep")
.chunk(100)
.reader(itemReader())
.outputChannel(requests()) // requests sent to workers
.inputChannel(replies()) // replies received from workers
.build();
}
// Middleware beans setup omitted
}
@Configuration
public static class WorkerConfiguration {
@Autowired
private RemoteChunkingWorkerBuilder workerBuilder;
@Bean
public IntegrationFlow workerFlow() {
return this.workerBuilder
.itemProcessor(itemProcessor())
.itemWriter(itemWriter())
.inputChannel(requests()) // requests received from the manager
.outputChannel(replies()) // replies sent to the manager
.build();
}
// Middleware beans setup omitted
}
}你可以在这里找到远程分块作业的完整示例。
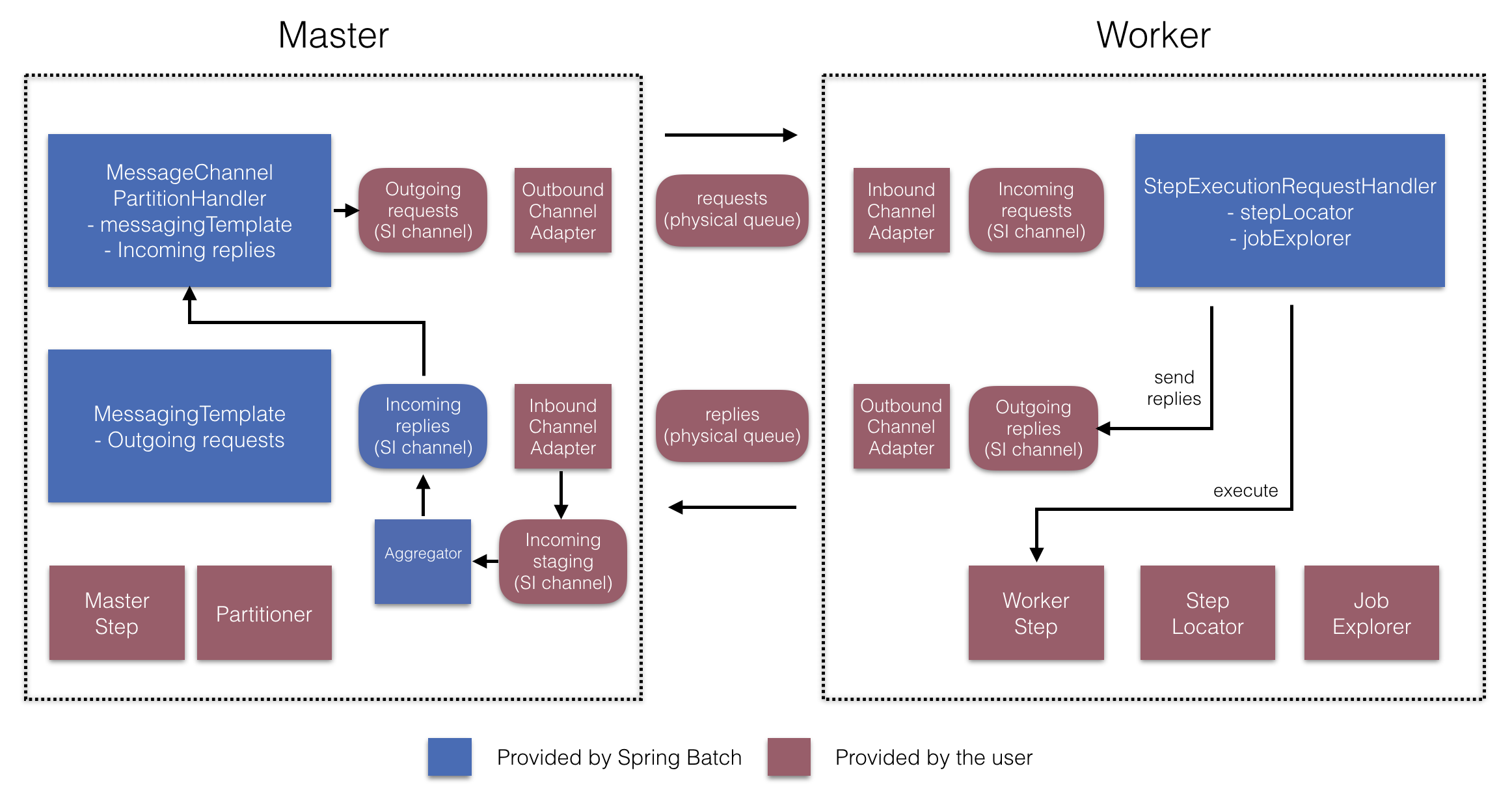
远程分区
下图展示了典型的远程分区情况:
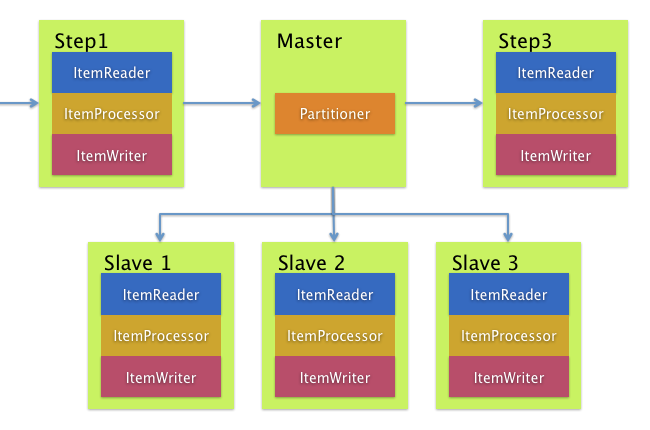
另一方面,远程分区在
不是处理项目本身,而是相关的输入输出
造成瓶颈。通过远程分区,你可以发送工作
给完成完整Spring Batch的工人
步骤。因此,每个工人都有自己的ItemReader,ItemProcessor和ItemWriter.为此,Spring Batch
积分提供MessageChannelPartitionHandler.
这种实现分区处理接口用途消息频道实例到
向远程工作者发送指令并接收他们的回复。
这很好地抽象了传输(如JMS)
以及AMQP)用于与远程工作者沟通。
“可扩展性”章节中涉及远程分区的部分概述了这些概念和
配置远程分区所需的组件,并显示
使用默认的示例任务执行者分区处理器划分
在独立的本地执行线程中。用于远程分区
对于多个JVM,则需要两个额外的组件:
-
远程织物或网格环境
-
一个
分区处理实现支持期望的 远程织物或网格环境
类似于远程分块,你可以用JMS作为“远程织物”。那就用
一个MessageChannelPartitionHandler实例分区处理实现
如前所述。
-
Java
-
XML
以下示例假设已有分区作业,重点关注MessageChannelPartitionHandler以及 Java 中的 JMS 配置:
/*
* Configuration of the manager side
*/
@Bean
public PartitionHandler partitionHandler() {
MessageChannelPartitionHandler partitionHandler = new MessageChannelPartitionHandler();
partitionHandler.setStepName("step1");
partitionHandler.setGridSize(3);
partitionHandler.setReplyChannel(outboundReplies());
MessagingTemplate template = new MessagingTemplate();
template.setDefaultChannel(outboundRequests());
template.setReceiveTimeout(100000);
partitionHandler.setMessagingOperations(template);
return partitionHandler;
}
@Bean
public QueueChannel outboundReplies() {
return new QueueChannel();
}
@Bean
public DirectChannel outboundRequests() {
return new DirectChannel();
}
@Bean
public IntegrationFlow outboundJmsRequests() {
return IntegrationFlow.from("outboundRequests")
.handle(Jms.outboundGateway(connectionFactory())
.requestDestination("requestsQueue"))
.get();
}
@Bean
@ServiceActivator(inputChannel = "inboundStaging")
public AggregatorFactoryBean partitioningMessageHandler() throws Exception {
AggregatorFactoryBean aggregatorFactoryBean = new AggregatorFactoryBean();
aggregatorFactoryBean.setProcessorBean(partitionHandler());
aggregatorFactoryBean.setOutputChannel(outboundReplies());
// configure other propeties of the aggregatorFactoryBean
return aggregatorFactoryBean;
}
@Bean
public DirectChannel inboundStaging() {
return new DirectChannel();
}
@Bean
public IntegrationFlow inboundJmsStaging() {
return IntegrationFlow
.from(Jms.messageDrivenChannelAdapter(connectionFactory())
.configureListenerContainer(c -> c.subscriptionDurable(false))
.destination("stagingQueue"))
.channel(inboundStaging())
.get();
}
/*
* Configuration of the worker side
*/
@Bean
public StepExecutionRequestHandler stepExecutionRequestHandler() {
StepExecutionRequestHandler stepExecutionRequestHandler = new StepExecutionRequestHandler();
stepExecutionRequestHandler.setJobExplorer(jobExplorer);
stepExecutionRequestHandler.setStepLocator(stepLocator());
return stepExecutionRequestHandler;
}
@Bean
@ServiceActivator(inputChannel = "inboundRequests", outputChannel = "outboundStaging")
public StepExecutionRequestHandler serviceActivator() throws Exception {
return stepExecutionRequestHandler();
}
@Bean
public DirectChannel inboundRequests() {
return new DirectChannel();
}
public IntegrationFlow inboundJmsRequests() {
return IntegrationFlow
.from(Jms.messageDrivenChannelAdapter(connectionFactory())
.configureListenerContainer(c -> c.subscriptionDurable(false))
.destination("requestsQueue"))
.channel(inboundRequests())
.get();
}
@Bean
public DirectChannel outboundStaging() {
return new DirectChannel();
}
@Bean
public IntegrationFlow outboundJmsStaging() {
return IntegrationFlow.from("outboundStaging")
.handle(Jms.outboundGateway(connectionFactory())
.requestDestination("stagingQueue"))
.get();
}以下示例假设已有分区作业,重点关注MessageChannelPartitionHandler以及 XML 中的 JMS 配置:
<bean id="partitionHandler"
class="org.springframework.batch.integration.partition.MessageChannelPartitionHandler">
<property name="stepName" value="step1"/>
<property name="gridSize" value="3"/>
<property name="replyChannel" ref="outbound-replies"/>
<property name="messagingOperations">
<bean class="org.springframework.integration.core.MessagingTemplate">
<property name="defaultChannel" ref="outbound-requests"/>
<property name="receiveTimeout" value="100000"/>
</bean>
</property>
</bean>
<int:channel id="outbound-requests"/>
<int-jms:outbound-channel-adapter destination="requestsQueue"
channel="outbound-requests"/>
<int:channel id="inbound-requests"/>
<int-jms:message-driven-channel-adapter destination="requestsQueue"
channel="inbound-requests"/>
<bean id="stepExecutionRequestHandler"
class="org.springframework.batch.integration.partition.StepExecutionRequestHandler">
<property name="jobExplorer" ref="jobExplorer"/>
<property name="stepLocator" ref="stepLocator"/>
</bean>
<int:service-activator ref="stepExecutionRequestHandler" input-channel="inbound-requests"
output-channel="outbound-staging"/>
<int:channel id="outbound-staging"/>
<int-jms:outbound-channel-adapter destination="stagingQueue"
channel="outbound-staging"/>
<int:channel id="inbound-staging"/>
<int-jms:message-driven-channel-adapter destination="stagingQueue"
channel="inbound-staging"/>
<int:aggregator ref="partitionHandler" input-channel="inbound-staging"
output-channel="outbound-replies"/>
<int:channel id="outbound-replies">
<int:queue/>
</int:channel>
<bean id="stepLocator"
class="org.springframework.batch.integration.partition.BeanFactoryStepLocator" />你还必须确保分区处理器属性映射到partitionHandler豆。
-
Java
-
XML
以下示例映射了该划分处理器归属于partitionHandler在
Java:
public Job personJob(JobRepository jobRepository) {
return new JobBuilder("personJob", jobRepository)
.start(new StepBuilder("step1.manager", jobRepository)
.partitioner("step1.worker", partitioner())
.partitionHandler(partitionHandler())
.build())
.build();
}以下示例映射了该划分处理器归属于partitionHandler在
XML:
<job id="personJob">
<step id="step1.manager">
<partition partitioner="partitioner" handler="partitionHandler"/>
...
</step>
</job>你可以在这里找到远程分区作业的完整示例。
你可以使用@EnableBatchIntegration注释以简化远程作
分区设置。该注释提供了两种对远程分区有用的豆子:
-
RemotePartitioningManagerStepBuilderFactory: 配置管理器步骤 -
RemotePartitioningWorkerStepBuilderFactory: 配置工人步骤
这些API负责配置多个组件,如下图所示:
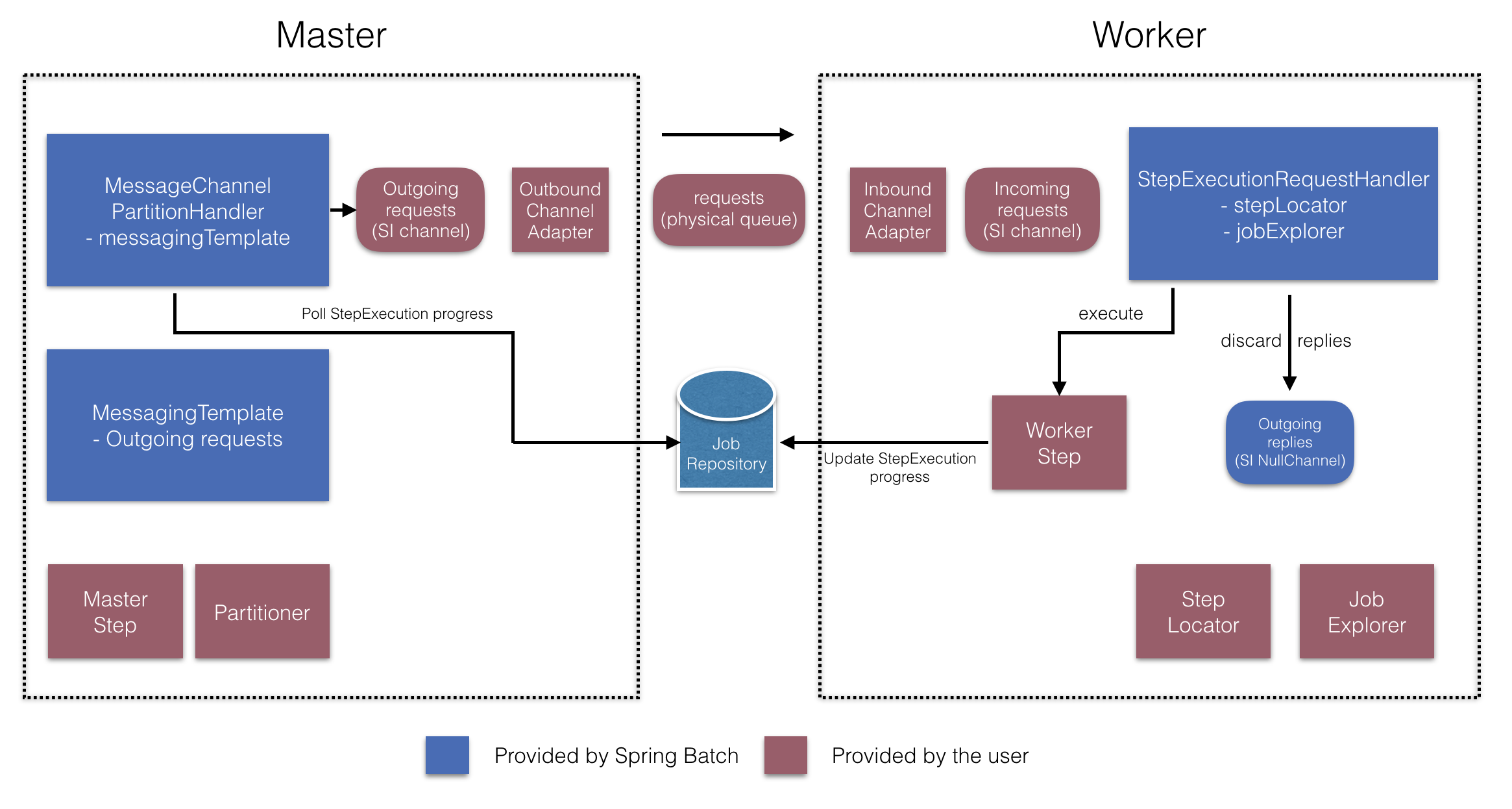
在经理方面,RemotePartitioningManagerStepBuilderFactory让你
通过声明配置管理器步骤:
-
这
分区器用于数据分区 -
用于向工人发送请求的输出通道(“发出请求”)
-
输入通道(“接收回复”)用于接收从工人处接收回复(配置回复聚合时)
-
轮询间隔和超时参数(配置作业仓库轮询时)
你不需要显式配置MessageChannelPartitionHandler以及消息模板.
(如果你有理由,仍然可以显式配置它们。)
在工人方面,RemotePartitioningWorkerStepBuilderFactory允许你配置工人:
-
监听管理器在输入通道发送的请求(“入站请求”)
-
呼叫
处理方法StepExecutionRequestHandler针对每个请求 -
在输出通道上向管理器发送回复(“发出回复”)
你不必显式配置StepExecutionRequestHandler.
(如果你有理由,可以明确配置它。)
以下示例展示了如何使用这些 API:
@Configuration
@EnableBatchProcessing
@EnableBatchIntegration
public class RemotePartitioningJobConfiguration {
@Configuration
public static class ManagerConfiguration {
@Autowired
private RemotePartitioningManagerStepBuilderFactory managerStepBuilderFactory;
@Bean
public Step managerStep() {
return this.managerStepBuilderFactory
.get("managerStep")
.partitioner("workerStep", partitioner())
.gridSize(10)
.outputChannel(outgoingRequestsToWorkers())
.inputChannel(incomingRepliesFromWorkers())
.build();
}
// Middleware beans setup omitted
}
@Configuration
public static class WorkerConfiguration {
@Autowired
private RemotePartitioningWorkerStepBuilderFactory workerStepBuilderFactory;
@Bean
public Step workerStep() {
return this.workerStepBuilderFactory
.get("workerStep")
.inputChannel(incomingRequestsFromManager())
.outputChannel(outgoingRepliesToManager())
.chunk(100)
.reader(itemReader())
.processor(itemProcessor())
.writer(itemWriter())
.build();
}
// Middleware beans setup omitted
}
}